作者: xiaoman
2023-03-01
这是CSS和CSS3的基础笔记.

h1 {
background-color: ##6495ed;
}
p {
background-color: ##e0ffff;
}
div {
background-color: ##b0c4de;
}body {
background-image: url("paper.gif");
}body {
background-image: url("gradient2.png");
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}background-attachment
background-position
body {
background-image: url("img_tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
}为
background-position属性提供值有很多方法。首先,可以使用一些关键字:top、bottom、left、right和center;**其次,可以使用长度值,如 100px 或 5cm;最后也可以使用百分数值。**不同类型的值对于背景图像的放置稍有差异。
h1 {
text-align: center;
}
p.date {
text-align: right;
}
p.main {
text-align: justify;
}h1 {
text-decoration: overline;
}
h2 {
text-decoration: line-through;
}
h3 {
text-decoration: underline;
}p.uppercase {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
p.lowercase {
text-transform: lowercase;
}
p.capitalize {
text-transform: capitalize;
}p {text-indent:50px;}word-spacing:30px;p {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}{font-style:normal|italic|oblique;}h1 {
font-size: 40px;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2.5em;
} /* 40px/16=2.5em */
/* 设置 <body>元素的默认字体大小的是百分比*/
body {
font-size: 100%;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2.5em;
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.875em;
}
p {
font-size: 0.875em;
}<a>a:link - 正常,未访问过的链接a:visited - 用户已访问过的链接a:hover - 当用户鼠标放在链接上时a:active - 链接被点击的那一刻a:link {color:##FF0000;} /* 未访问链接*/
a:visited {color:##00FF00;} /* visited link */
a:hover {color:##FF00FF;} /* mouse over link */
a:active {color:##0000FF;} /* selected link */
a:hover必须跟在a:link和a:visited后面a:active必须跟在a:hover后面
a:link {
text-decoration: none;
}
a:visited {
text-decoration: none;
}
a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
a:active {
text-decoration: underline;
}a:link {
background-color: ##b2ff99;
}
a:visited {
background-color: ##ffff85;
}
a:hover {
background-color: ##ff704d;
}
a:active {
background-color: ##ff704d;
}| 属性值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| default | 默认光标,箭头 |
| pointer | 超链接的指针,手型 |
| wait | 指示程序正在忙 |
| help | 指示可用的帮忙 |
| text | 指示文本 |
| crosshair | 鼠标呈现十字状 |
a:hover {
color: green;
cursor: crosshair;
}none:不使用项目符号disc:实心圆circle:空心圆square:实心方块decimal:阿拉伯数字lower-alpha:小写英文字母upper-alpha:大写英文字母lower-roman:小写罗马数字upper-roman:大写罗马数字ul.a {
list-style-type: circle;
}
ul.b {
list-style-type: square;
}
ol.c {
list-style-type: upper-roman;
}
ol.d {
list-style-type: lower-alpha;
}table,
th,
td {
border: 1px solid black;
}table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table,
th,
td {
border: 1px solid black;
}width heighttable {
width: 100%;
}
th {
height: 50px;
}td { text-align:right; } 文本对齐
td
{ height:50px; vertical-align:bottom; } 垂直对齐td { padding:15px; }table,
td,
th {
border: 1px solid green;
}
th {
background-color: green;
color: white;
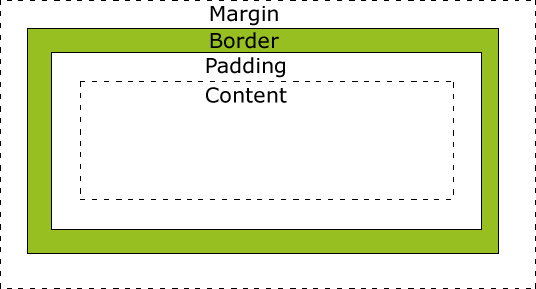
}所有 HTML 元素可以看作盒子,在 CSS 中,“box model “这一术语是用来设计和布局时使用。
CSS 盒模型本质上是一个盒子,封装周围的 HTML 元素,它包括:边距,边框,填充,和实际内容。
盒模型允许我们在其它元素和周围元素边框之间的空间放置元素。

不同部分的说明:
元素的宽度和高度
重要: 当您指定一个 CSS 元素的宽度和高度属性时,你只是设置内容区域的宽度和高度。要知道,完全大小的元素,你还必须添加填充,边框和边距。 下面的例子中的元素的总宽度为 300px
width:250px;
padding:10px;
border:5px solid gray;
margin:10px;250px (宽) + 20px (左 + 右填充) + 10px (左 + 右边框) + 20px (左 + 右边距) = 300px
总宽度为 250 像素的元素
width: 220px;
padding: 10px;
border: 5px solid gray;
margin: 0px;浏览器的兼容性问题
一旦为页面设置了恰当的 DTD,大多数浏览器都会按照上面的图示来呈现内容。然而 IE 5 和 6 的呈现却是不正确的。根据 W3C 的规范,元素内容占据的空间是由 width 属性设置的,而内容周围的 padding 和 border 值是另外计算的。不幸的是,IE5.X 和 6 在怪异模式中使用自己的非标准模型。这些浏览器的 width 属性不是内容的宽度,而是内容、内边距和边框的宽度的总和。
虽然有方法解决这个问题。但是目前最好的解决方案是回避这个问题。也就是,不要给元素添加具有指定宽度的内边距,而是尝试将内边距或外边距添加到元素的父元素和子元素。
IE8 及更早 IE 版本不支持 填充的宽度和边框的宽度属性设。
解决 IE8 及更早版本不兼容问题可以在 HTML 页面声明 <!DOCTYPE html>即可。
边框指定宽度有两种方法:可以指定长度值,比如 2px 或 0.1em
p.one {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 5px;
}
p.two {
border-style: solid;
border-width: medium;
}注意: border-color 单独使用是不起作用的,必须得先使用 border-style 来设置边框样式。
p.one {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
}
p.two {
border-style: solid;
border-color: ##98bf21;
}在 CSS 中,可以指定不同的侧面不同的边框
p {
border-top-style: dotted;
border-right-style: solid;
border-bottom-style: dotted;
border-left-style: solid;
}a:link, a:visited {
border-style: solid; border-width: 5px; border-color: transparent;
} a:hover {border-color: gray;}利用 transparent,使用边框就像是额外的内边距一样;此外还有一个好处,就是能在你需要的时候使其可见。这种透明边框相当于内边距,因为元素的背景会延伸到边框区域(如果有可见背景的话)。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| border | 简写属性,用于把针对四个边的属性设置在一个声明。 |
| border-style | 用于设置元素所有边框的样式,或者单独地为各边设置边框样式。 |
| border-width | 简写属性,用于为元素的所有边框设置宽度,或者单独地为各边边框设置宽度。 |
| border-color | 简写属性,设置元素的所有边框中可见部分的颜色,或为 4 个边分别设置颜色。 |
| border-bottom | 简写属性,用于把下边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-bottom-color | 设置元素的下边框的颜色。 |
| border-bottom-style | 设置元素的下边框的样式。 |
| border-bottom-width | 设置元素的下边框的宽度。 |
| border-left | 简写属性,用于把左边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-left-color | 设置元素的左边框的颜色。 |
| border-left-style | 设置元素的左边框的样式。 |
| border-left-width | 设置元素的左边框的宽度。 |
| border-right | 简写属性,用于把右边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-right-color | 设置元素的右边框的颜色。 |
| border-right-style | 设置元素的右边框的样式。 |
| border-right-width | 设置元素的右边框的宽度。 |
| border-top | 简写属性,用于把上边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-top-color | 设置元素的上边框的颜色。 |
| border-top-style | 设置元素的上边框的样式。 |
| border-top-width | 设置元素的上边框的宽度。 |
CSS 轮廓(outline)
轮廓(outline)是绘制于元素周围的一条线,位于边框边缘的外围,可起到突出元素的作用

所有 CSS 轮廓(outline)属性
| 属性 | 说明 | 值 | CSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| outline | 在一个声明中设置所有的外边框属性 | outline-color outline-style outline-width inherit | 2 |
| outline-color | 设置外边框的颜色 | color-name hex-number rgb-number invert inherit | 2 |
| outline-style | 设置外边框的样式 | none dotted dashed solid double groove ridge inset outset inherit | 2 |
| outline-width | 设置外边框的宽度 | thin medium thick length inherit | 2 |
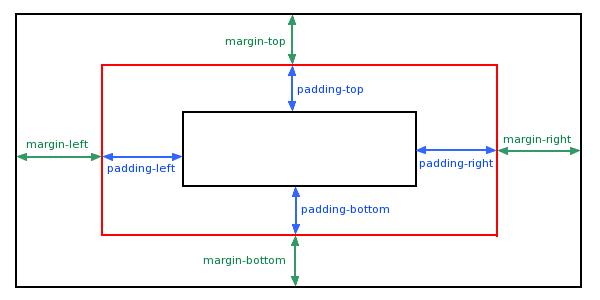
margin 清除周围的元素(外边框)的区域。margin 没有背景颜色,是完全透明的
margin 可以单独改变元素的上,下,左,右边距。也可以一次改变所有的属性。
| 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| auto | 设置浏览器边距。 这样做的结果会依赖于浏览器 |
| length | 定义一个固定的 margin(使用像素,pt,em 等) |
| % | 定义一个使用百分比的边距 |
em 和 px 是 CSS 中常用的长度单位。px 是像素,是相对于显示器屏幕分辨率的单位,而 em 是相对于父元素的字体大小的单位。
具体来说,1em 等于父元素的字体大小,比如如果父元素的字体大小为 16px,那么子元素设置为 1em 就相当于 16px。如果子元素嵌套了一个子元素,那么这个子元素的字体大小就是根据父元素的字体大小计算的。
因此,em 的大小是相对于父元素的字体大小而言的,而 px 的大小是固定的。使用 em 作为长度单位可以使得网页在不同的设备和屏幕上显示更为一致,而使用 px 则可以精确控制元素的大小。
Margin 可以使用负值,重叠的内容。
当元素的 Padding(填充)(内边距)被清除时,所”释放”的区域将会受到元素背景颜色的填充。
单独使用填充属性可以改变上下左右的填充。缩写填充属性也可以使用,一旦改变一切都改变。

| 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| length | 定义一个固定的填充(像素, pt, em,等) |
| % | 使用百分比值定义一个填充 |
**提示:**CSS padding 属性可以使用长度值或百分比值,但与 margin 属性不同,它不允许使用负值。
p {
padding: 20%;
}注意:上下内边距与左右内边距一致,即上下内边距的百分数会相对于父元素宽度设置,而不是相对于高度。
padding-top: 25px;
padding-bottom: 25px;
padding-right: 50px;
padding-left: 50px;padding:25px 50px;Padding 属性,可以有一到四个值。
padding:25px 50px 75px 100px;
上填充为25px
右填充为50px
下填充为75px
左填充为100px
padding:25px 50px 75px;
上填充为25px
左右填充为50px
下填充为75px
padding:25px 50px;
上下填充为25px
左右填充为50px
padding:25px;
所有的填充都是25pxh1,
h2,
p {
color: green;
}p{ }: 为所有 p 元素指定一个样式。.marked{ }: 为所有 class=“marked” 的元素指定一个样式。.marked p{ }: 为所有 class=“marked” 元素内的 p 元素指定一个样式。p.marked{ }: 为所有 class=“marked” 的 p 元素指定一个样式。p {
color: blue;
text-align: center;
}
.marked {
background-color: red;
}
.marked p {
color: white;
}
p.marked {
text-decoration: underline;
}h1.hidden {visibility:hidden;} 不可见
h1.hidden {display:none;} 不显示块元素是一个元素,占用了全部宽度,在前后都是换行符。
<h1><p><div>
内联元素只需要必要的宽度,不强制换行。
<span> <a>li {display:inline;}span {display:block;}position 属性指定了元素的定位类型。 position 属性的五个值:
HTML 元素的默认值,即没有定位,遵循正常的文档流对象。 静态定位的元素不会受到 top, bottom, left, right 影响。
div.static {
position: static;
border: 3px solid ##73ad21;
}元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。 即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动:
p.pos_fixed {
position: fixed;
top: 30px;
right: 5px;
}相对定位元素的定位是相对其正常位置。
h2.pos_left {
position: relative;
left: -20px;
}
h2.pos_right {
position: relative;
left: 20px;
}
h2.pos_top {
position: relative;
top: -50px;
}绝对定位的元素的位置相对于最近的已定位父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>
h2 {
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 150px;
}absolute 定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。 absolute 定位的元素和其他元素重叠。
sticky 英文字面意思是粘,粘贴,所以可以把它称之为粘性定位。 position: sticky ; 基于用户的滚动位置来定位。 粘性定位的元素是依赖于用户的滚动,在 position: relative 与 position:fixed 定位之间切换。 它的行为就像 position: relative ; 而当页面滚动超出目标区域时,它的表现就像 position:fixed;,它会固定在目标位置。 元素定位表现为在跨越特定阈值前为相对定位,之后为固定定位。 这个特定阈值指的是 top, right, bottom 或 left 之一,换言之,指定 top, right, bottom 或 left 四个阈值其中之一,才可使粘性定位生效。否则其行为与相对定位相同。 注意: Internet Explorer , Edge 15 及更早 IE 版本不支持 sticky 定位。 Safari 需要使用 -webkit- prefix (查看以下实例)。
div. sticky {
position: -webkit-sticky; /* Safari */
position: sticky;
top: 0;
background-color: green;
border: 2px solid ##4caf50;
}元素的定位与文档流无关,所以它们可以覆盖页面上的其它元素 z-index 属性指定了一个元素的堆叠顺序(哪个元素应该放在前面,或后面) 一个元素可以有正数或负数的堆叠顺序
img {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
z-index: -1;
}CSS overflow 属性可以控制内容溢出元素框时在对应的元素区间内添加滚动条。 overflow 属性有以下值:
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| visible | 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。 |
| hidden | 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的。 |
| scroll | 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| auto | 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。 |
注意:overflow 属性只工作于指定高度的块元素上。 注意: 在 OS X Lion ( Mac 系统) 系统上,滚动条默认是隐藏的,使用的时候才会显示 (设置 “overflow:scroll” 也是一样的)。
默认情况下,overflow 的值为 visible, 意思是内容溢出元素框
div {
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
background-color: ##eee;
overflow: visible;
}元素的水平方向浮动,意味着元素只能左右移动而不能上下移动。 一个浮动元素会尽量向左或向右移动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。 浮动元素之后的元素将围绕它。 浮动元素之前的元素将不会受到影响。 如果图像是右浮动,下面的文本流将环绕在它左边
img {
float: right;
}如果你把几个浮动的元素放到一起,如果有空间的话,它们将彼此相邻。 在这里,我们对图片廊使用 float 属性
.thumbnail {
float: left;
width: 110px;
height: 90px;
margin: 5px;
}元素浮动之后,周围的元素会重新排列,为了避免这种情况,使用 clear 属性。 clear 属性指定元素两侧不能出现浮动元素
.text_line {
clear: both;
}要水平居中对齐一个元素(如<div>), 可以使用 margin: auto;。
设置到元素的宽度将防止它溢出到容器的边缘。
元素通过指定宽度,并将两边的空外边距平均分配
.center {
margin: auto;
width: 50%;
border: 3px solid green;
padding: 10px;
}文本在元素内居中对齐,可以使用 text-align: center;
要让图片居中对齐, 可以使用 margin: auto; 并将它放到 块 元素中
img {
display: block;
margin: auto;
width: 40%;
}我们可以使用 position: absolute; 属性来对齐元素
.right {
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
width: 300px;
border: 3px solid ##73ad21;
padding: 10px;
}注释:绝对定位元素会被从正常流中删除,并且能够交叠元素。
提示: 当使用 position 来对齐元素时, 通常 <body> 元素会设置 margin 和 padding 。 这样可以避免在不同的浏览器中出现可见的差异。
当使用 position 属性时,IE8 以及更早的版本存在一个问题。如果容器元素(在我们的案例中是 <div class="container">)设置了指定的宽度,并且省略了 !DOCTYPE 声明,那么 IE8 以及更早的版本会在右侧增加 17px 的外边距。这似乎是为滚动条预留的空间。当使用 position 属性时,请始终设置 !DOCTYPE 声明:body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
}
.right {
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
width: 300px;
background-color: ##b0e0e6;
}我们也可以使用 float 属性来对齐元素
.right {
float: right;
width: 300px;
border: 3px solid ##73ad21;
padding: 10px;
}当像这样对齐元素时,对 <body> 元素的外边距和内边距进行预定义是一个好主意。这样可以避免在不同的浏览器中出现可见的差异。
注意:如果子元素的高度大于父元素,且子元素设置了浮动,那么子元素将溢出,这时候你可以使用 “clearfix(清除浮动)” 来解决该问题。 我们可以在父元素上添加
overflow: auto;来解决子元素溢出的问题:
.clearfix {
overflow: auto;
}当使用 float 属性时,IE8 以及更早的版本存在一个问题。如果省略 !DOCTYPE 声明,那么 IE8 以及更早的版本会在右侧增加 17px 的外边距。这似乎是为滚动条预留的空间。当使用 float 属性时,请始终设置 !DOCTYPE 声明:
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.right {
float: right;
width: 300px;
background-color: ##b0e0e6;
}CSS 中有很多方式可以实现垂直居中对齐。 一个简单的方式就是头部顶部使用 padding:
.center {
padding: 70px 0;
border: 3px solid green;
}如果要水平和垂直都居中,可以使用 padding 和 text-align: center:
.center {
padding: 70px 0;
border: 3px solid green;
text-align: center;
}.center {
line-height: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid green;
text-align: center;
}
/* 如果文本有多行,添加以下代码: */
.center p {
line-height: 1.5;
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: middle;
}除了使用 padding 和 line-height 属性外,我们还可以使用 transform 属性来设置垂直居中:
.center {
height: 200px;
position: relative;
border: 3px solid green;
}
.center p {
margin: 0;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}组合选择符说明了两个选择器之间的关系。 CSS 组合选择符包括各种简单选择符的组合方式。 在 CSS3 中包含了四种组合方式:
后代选择器用于选取某元素的后代元素。
以下实例选取所有 <p> 元素插入到 <div> 元素中:
div p {
background-color: yellow;
}与后代选择器相比,子元素选择器(Child selectors)只能选择作为某元素直接/一级子元素的元素
div > p {
background-color: yellow;
}相邻兄弟选择器(Adjacent sibling selector)可选择紧接在另一元素后的元素,且二者有相同父元素。 如果需要选择紧接在另一个元素后的元素,而且二者有相同的父元素,可以使用相邻兄弟选择器(Adjacent sibling selector)
div + p {
background-color: yellow;
}后续兄弟选择器选取所有指定元素之后的相邻兄弟元素
div ~ p {
background-color: yellow;
}CSS 伪类是用来添加一些选择器的特殊效果
伪类的语法:
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}CSS 类也可以使用伪类:
selector.class:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}在支持 CSS 的浏览器中,链接的不同状态都可以以不同的方式显示
a:link {
color: ##ff0000;
} /* 未访问的链接 */
a:visited {
color: ##00ff00;
} /* 已访问的链接 */
a:hover {
color: ##ff00ff;
} /* 鼠标划过链接 */
a:active {
color: ##0000ff;
} /* 已选中的链接 */注意: 在 CSS 定义中,a:hover 必须被置于 a:link 和 a:visited 之后,才是有效的。 注意: 在 CSS 定义中,a:active 必须被置于 a:hover 之后,才是有效的。 注意:伪类的名称不区分大小写。
伪类可以与 CSS 类配合使用
a.red:visited {color:##FF0000;}
<a class="red" href="css-syntax.html">CSS 语法</a>您可以使用 :first-child 伪类来选择父元素的第一个子元素。
<p> 元素在下面的例子中,选择器匹配作为任何元素的第一个子元素的 <p> 元素
p:first-child {
color: blue;
}<p> 元素中的第一个 <i> 元素在下面的例子中,选择相匹配的所有<p>元素的第一个 <i> 元素
p > i:first-child {
color: blue;
}<p> 元素中的所有 <i> 元素在下面的例子中,选择器匹配所有作为元素的第一个子元素的 <p> 元素中的所有 <i> 元素
p:first-child i {
color: blue;
}:lang 伪类使你有能力为不同的语言定义特殊的规则 **注意:**IE8 必须声明才能支持;lang 伪类。
在下面的例子中,:lang 类为属性值为 no 的 q 元素定义引号的类型:
q:lang(no) {
quotes: "~""~";
}| 选择器 | 示例 | 示例说明 |
|---|---|---|
| :checked | input:checked | 选择所有选中的表单元素 |
| :disabled | input:disabled | 选择所有禁用的表单元素 |
| :empty | p:empty | 选择所有没有子元素的 p 元素 |
| :enabled | input:enabled | 选择所有启用的表单元素 |
| :first-of-type | p:first-of-type | 选择的每个 p 元素是其父元素的第一个 p 元素 |
| :in-range | input:in-range | 选择元素指定范围内的值 |
| :invalid | input:invalid | 选择所有无效的元素 |
| :last-child | p:last-child | 选择所有 p 元素的最后一个子元素 |
| :last-of-type | p:last-of-type | 选择每个 p 元素是其母元素的最后一个 p 元素 |
| :not(selector) | :not(p) | 选择所有 p 以外的元素 |
| :nth-child(n) | p:nth-child(2) | 选择所有 p 元素的父元素的第二个子元素 |
| :nth-last-child(n) | p:nth-last-child(2) | 选择所有 p 元素倒数的第二个子元素 |
| :nth-last-of-type(n) | p:nth-last-of-type(2) | 选择所有 p 元素倒数的第二个为 p 的子元素 |
| :nth-of-type(n) | p:nth-of-type(2) | 选择所有 p 元素第二个为 p 的子元素 |
| :only-of-type | p:only-of-type | 选择所有仅有一个子元素为 p 的元素 |
| :only-child | p:only-child | 选择所有仅有一个子元素的 p 元素 |
| :optional | input:optional | 选择没有”required”的元素属性 |
| :out-of-range | input:out-of-range | 选择指定范围以外的值的元素属性 |
| :read-only | input:read-only | 选择只读属性的元素属性 |
| :read-write | input:read-write | 选择没有只读属性的元素属性 |
| :required | input:required | 选择有”required”属性指定的元素属性 |
| :root | root | 选择文档的根元素 |
| :target | ##news:target | 选择当前活动##news 元素(点击 URL 包含锚的名字) |
| :valid | input:valid | 选择所有有效值的属性 |
| :link | a:link | 选择所有未访问链接 |
| :visited | a:visited | 选择所有访问过的链接 |
| :active | a:active | 选择正在活动链接 |
| :hover | a:hover | 把鼠标放在链接上的状态 |
| :focus | input:focus | 选择元素输入后具有焦点 |
| :first-letter | p:first-letter | 选择每个<p> 元素的第一个字母 |
| :first-line | p:first-line | 选择每个<p> 元素的第一行 |
| :first-child | p:first-child | 选择器匹配属于任意元素的第一个子元素的 <p> 元素 |
| :before | p:before | 在每个<p>元素之前插入内容 |
| :after | p:after | 在每个<p>元素之后插入内容 |
| :lang(language) | p:lang(it) | 为<p>元素的 lang 属性选择一个开始值 |
CSS 伪元素是用来添加一些选择器的特殊效果。 CSS 伪元素控制的内容和元素是没有差别的,但是它本身只是基于元素的抽象,并不存在于文档中,所以称为伪元素。
selector:pseudo-element {
property: value;
}selector.class:pseudo-element {
property: value;
}在 CSS1 和 CSS2 中,伪元素和伪类都采用单冒号进行表示,在 CSS3 中为了区分伪元素和伪类,规定使用双冒号代表伪元素,单冒号代表伪类,即 CSS3 标准中应该这么写:
selector.class::pseudo-element {property:value;}
虽然 CSS3 规定了必须使用双冒号,但实际上使用单冒号也可以工作,这是由于 CSS 的兼容性带来的,但这并不意味着可以无所忌惮的使用单冒号,因为单双冒号的区分,可以给 CSS 代码带来更高的可读性。
first-line 伪元素用于向文本的首行设置特殊样式
p:first-line {
color: ##ff0000;
font-variant: small-caps;
}注意:“first-line” 伪元素只能用于块级元素。 注意: 下面的属性可应用于 “first-line” 伪元素:
- font properties
- color properties
- background properties
- word-spacing
- letter-spacing
- text-decoration
- vertical-align
- text-transform
- line-height
- clear“first-letter” 伪元素用于向文本的首字母设置特殊样式
p:first-letter {
color: ##ff0000;
font-size: xx-large;
}伪元素可以结合 CSS 类
p.article:first-letter {color:##ff0000;}
<p class="article">A paragraph in an article</p>可以结合多个伪元素来使用。 在下面的例子中,段落的第一个字母将显示为红色,其字体大小为 xx-large。第一行中的其余文本将为蓝色,并以小型大写字母显示。 段落中的其余文本将以默认字体大小和颜色来显示
p:first-letter {
color: ##ff0000;
font-size: xx-large;
}
p:first-line {
color: ##0000ff;
font-variant: small-caps;
}:before 伪元素可以在元素的内容前面插入新内容。
下面的例子在每个 <h1>元素前面插入一幅图片
h1:before {
content: url(smiley.gif);
}:after 伪元素可以在元素的内容之后插入新内容。
下面的例子在每个 <h1>元素后面插入一幅图片
h1:after {
content: url(smiley.gif);
}| 选择器 | 示例 | 示例说明 |
|---|---|---|
| :link | a:link | 选择所有未访问链接 |
| :visited | a:visited | 选择所有访问过的链接 |
| :active | a:active | 选择正在活动链接 |
| :hover | a:hover | 把鼠标放在链接上的状态 |
| :focus | input:focus | 选择元素输入后具有焦点 |
| :first-letter | p:first-letter | 选择每个 p 元素的第一个字母 |
| :first-line | p:first-line | 选择每个 p 元素的第一行 |
| :first-child | p:first-child | 选择器匹配属于任意元素的第一个子元素的 ]p> 元素 |
| :before | p:before | 在每个 p 元素之前插入内容 |
| :after | p:after | 在每个 p 元素之后插入内容 |
| :lang(language) | p:lang(it) | 为 p 元素的 lang 属性选择一个开始值 |
作为标准的 HTML 基础一个导航栏是必须的。
在我们的例子中我们将建立一个标准的 HTML 列表导航栏。
导航条基本上是一个链接列表,所以使用 <ul> 和 <li> 元素非常有意义
<ul>
<li><a href="default.asp">主页</a></li>
<li><a href="news.asp">新闻</a></li>
<li><a href="contact.asp">联系</a></li>
<li><a href="about.asp">关于</a></li>
</ul>删除边距和填充
ul {
list-style-type: none;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}list-style-type:none - 移除列表前小标志。一个导航栏并不需要列表标记将上面代码做一下修改便可得垂直导航栏
a
{
display:block; <* 将内容显示为块 *>
width:60px;
}有两种方法创建横向导航栏。使用内联或浮动的列表项。 这两种方法都很好,但如果你想链接到具有相同的大小,你必须使用浮动的方法 ######################## 内嵌列表项
li {
display: inline;
}######################## 浮动列表项
li {
float: left;
}
a {
display: block;
width: 60px;
}float:left - 使用浮动块元素的幻灯片彼此相邻display:block - 显示块元素的链接,让整体变为可点击链接区域(不只是文本),它允许我们指定宽度display:inline; -默认情况下,元素是块元素。在这里,我们删除换行符之前和之后每个列表项,以显示一行 。<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>下拉菜单实例|W3Cschool教程(w3cschool.cn)</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<style>
.dropdown {
position: relative;
display: inline-block;
}
.dropdown-content {
display: none;
position: absolute;
background-color: ##f9f9f9;
min-width: 160px;
box-shadow: 0px 8px 16px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
padding: 12px 16px;
}
.dropdown:hover .dropdown-content {
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>鼠标移动后出现下拉菜单</h2>
<p>将鼠标移动到指定元素上就能看到下拉菜单。</p>
<div class="dropdown">
<span>鼠标移动到我这!</span>
<div class="dropdown-content">
<p>W3Cschool教程</p>
<p>www.w3cschool.cn</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>HTML 部分:
我们可以使用任何的 HTML 元素来打开下拉菜单,如:<span>, 或 a <button> 元素。
使用容器元素 (如: <div>) 来创建下拉菜单的内容,并放在任何你想放的位置上。
使用 <div> 元素来包裹这些元素,并使用 CSS 来设置下拉内容的样式。
CSS 部分:
.dropdown 类使用 position:relative, 这将设置下拉菜单的内容放置在下拉按钮 (使用 position:absolute) 的右下角位置。
.dropdown-content 类中是实际的下拉菜单。默认是隐藏的,在鼠标移动到指定元素后会显示。 注意 min-width 的值设置为 160px。你可以随意修改它。 注意: 如果你想设置下拉内容与下拉按钮的宽度一致,可设置 width 为 100% ( overflow:auto 设置可以在小尺寸屏幕上滚动)。
我们使用 box-shadow 属性让下拉菜单看起来像一个”卡片”。
:hover 选择器用于在用户将鼠标移动到下拉按钮上时显示下拉菜单。
<style>
/* 容器 <div> - 需要定位下拉内容 */
.dropdown {
position: relative;
display: inline-block; }
/* 下拉内容 (默认隐藏) */
.dropdown-content {
display: none;
position: absolute; }
/* 下拉菜单的链接 */
.dropdown-content a {
text-decoration: none;
display: block; }
/* 鼠标移上去后修改下拉菜单链接颜色 */
.dropdown-content a:hover {background-color: ##f1f1f1}
/* 在鼠标移上去后显示下拉菜单 */
.dropdown:hover .dropdown-content {
display: block; }
/* 当下拉内容显示后修改下拉按钮的背景颜色 */
.dropdown:hover .dropbtn {
background-color: ##3e8e41; }
</style>下拉内容对齐方式
float: left;
float: right;<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>W3Cschool教程(w3cschool.cn)</title>
<style>
div.img {
margin: 2px;
border: 1px solid ##000000;
height: auto;
width: auto;
float: left;
text-align: center;
}
div.img img {
display: inline;
margin: 3px;
border: 1px solid ##ffffff;
}
div.img a:hover img {
border: 1px solid ##0000ff;
}
div.desc {
text-align: center;
font-weight: normal;
width: 120px;
margin: 2px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="javascript;:"
><img
src="/statics/images/course/klematis_small.jpg"
alt="Klematis"
width="110"
height="90"
/></a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="javascript;:"
><img
src="/statics/images/course/klematis2_small.jpg"
alt="Klematis"
width="110"
height="90"
/></a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="javascript;:"
><img
src="/statics/images/course/klematis3_small.jpg"
alt="Klematis"
width="110"
height="90"
/></a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="javascript;:"
><img
src="/statics/images/course/klematis4_small.jpg"
alt="Klematis"
width="110"
height="90"
/></a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>img
{ opacity:0.4; filter:alpha(opacity=40); /*IE8 及更早版本 */ }@media 规则允许在相同样式表为不同媒体设置不同的样式。
在下面的例子告诉我们浏览器屏幕上显示一个 14 像素的 Verdana 字体样式。但是如果页面打印,将是 10 个像素的 Times 字体。请注意,font-weight在屏幕上和纸上设置为粗体
<style>
@media screen
{ p.test {font-family:verdana,sans-serif;font-size:14px; } }
@media print
{ p.test {font-family:times,serif;font-size:10px;} }
@media screen,print
{ p.test {font-weight:bold;}}
</style>顾名思义,CSS 属性选择器就是指可以根据元素的属性以及属性值来选择元素。 把包含标题(title)的所有元素变为蓝色
[title] {
color: blue;
}改变了标题 title='w3cschool' 元素的边框样式
[title="w3cschool"] {
border: 5px solid green;
}包含指定值的 title 属性的元素样式的例子,使用(~)分隔属性和值
[title~="hello"] {
color: blue;
}
[lang|="en"] {
color: blue;
}input[type="text"] {
width: 150px;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 10px;
background-color: yellow;
}
input[type="button"] {
width: 120px;
margin-left: 35px;
display: block;
}很多网页都是基于网格设计的,这说明网页是按列来布局的。
 使用网格视图有助于我们设计网页。这让我们向网页添加元素变的更简单。
使用网格视图有助于我们设计网页。这让我们向网页添加元素变的更简单。
 响应式网格视图通常是 12 列,宽度为 100%,在浏览器窗口大小调整时会自动伸缩。
响应式网格视图
响应式网格视图通常是 12 列,宽度为 100%,在浏览器窗口大小调整时会自动伸缩。
响应式网格视图
接下来我们来创建一个响应式网格视图。 首先确保所有的 HTML 元素都有 box-sizing 属性且设置为 border-box。 确保边距和边框包含在元素的宽度和高度间。 添加如下代码:
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}.menu {
width: 25%;
float: left;
}
.main {
width: 75%;
float: left;
}以上实例包含两列。 12 列的网格系统可以更好的控制响应式网页。 首先我们可以计算每列的百分比: 100% / 12 列 = 8.33%。 在每列中指定 class, class=“col-” 用于定义每列有几个 span :
.col-1 {
width: 8.33%;
}
.col-2 {
width: 16.66%;
}
.col-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-4 {
width: 33.33%;
}
.col-5 {
width: 41.66%;
}
.col-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-7 {
width: 58.33%;
}
.col-8 {
width: 66.66%;
}
.col-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-10 {
width: 83.33%;
}
.col-11 {
width: 91.66%;
}
.col-12 {
width: 100%;
}所有的列向左浮动,间距(padding) 为 15px:
[class*="col-"] {
float: left;
padding: 15px;
border: 1px solid red;
}每一行使用 <div> 包裹。所有列数加起来应为 12:
<div class="row">
<div class="col-3">...</div>
<div class="col-9">...</div>
</div列中行为左浮动,并添加清除浮动:
.row:after {
content: "";
clear: both;
display: block;
}我们可以添加一些样式和颜色,让其更好看:
.header {
background-color: ##9933cc;
color: ##ffffff;
padding: 15px;
}
.menu li {
padding: 8px;
margin-bottom: 7px;
background-color: ##33b5e5;
color: ##ffffff;
box-shadow: 0 1px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.12), 0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.24);
}
.menu li:hover {
background-color: ##0099cc;
}如果浏览器窗口小于 500px,
背景将变为浅蓝色: @media only screen and (max-width: 500px) {
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
}在先前的教程中我们使用行和列来制作网页,它是响应式的,但在小屏幕上并不能友好的展示。
媒体查询可以帮我们解决这个问题。我们可以在设计稿的中间添加断点,不同的断点有不同的效果。
######################## 桌面设备

######################## 手机设备

使用媒体查询在 768px 添加断点:
当屏幕(浏览器窗口)小于768px,每一列的宽度是100%:
/* For desktop: */ .col-1 {
width: 8.33%;
}
.col-2 {
width: 16.66%;
}
.col-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-4 {
width: 33.33%;
}
.col-5 {
width: 41.66%;
}
.col-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-7 {
width: 58.33%;
}
.col-8 {
width: 66.66%;
}
.col-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-10 {
width: 83.33%;
}
.col-11 {
width: 91.66%;
}
.col-12 {
width: 100%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
/* For mobile phones: */
[class*="col-"] {
width: 100%;
}
}移动端优先意味着在设计桌面和其他设备时优先考虑移动端的设计。 这就意味着我们必须对 CSS 做一些改变。 我们在屏幕小于 768px 进行样式修改,同样在屏幕宽度大于 768px 时也需要修改样式。以下是移动端优先实例
/* 为移动端设计: */
[class*="col-"] {
width: 100%;
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
/* For desktop: */
.col-1 {
width: 8.33%;
}
.col-2 {
width: 16.66%;
}
.col-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-4 {
width: 33.33%;
}
.col-5 {
width: 41.66%;
}
.col-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-7 {
width: 58.33%;
}
.col-8 {
width: 66.66%;
}
.col-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-10 {
width: 83.33%;
}
.col-11 {
width: 91.66%;
}
.col-12 {
width: 100%;
}
}你可以根据自己的需要添加断点。
我们同样可以为平板设备和移动手机设备设置断点。
######################## 桌面设备
 ######################## 平板设备
######################## 平板设备
 ######################## 手机设备
######################## 手机设备
 在屏幕为 600px 时添加媒体查询,并设置新的样式(屏幕大于 600px 但小于 768px)
在屏幕为 600px 时添加媒体查询,并设置新的样式(屏幕大于 600px 但小于 768px)
注意两组类样式是相同的,但名称不同(col- 和 col-m-):
/* For mobile phones: */ [class * = "col-" ] {
width: 100%;
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 600px) {
/* For tablets: */
.col-m-1 {
width: 8.33%;
}
.col-m-2 {
width: 16.66%;
}
.col-m-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-m-4 {
width: 33.33%;
}
.col-m-5 {
width: 41.66%;
}
.col-m-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-m-7 {
width: 58.33%;
}
.col-m-8 {
width: 66.66%;
}
.col-m-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-m-10 {
width: 83.33%;
}
.col-m-11 {
width: 91.66%;
}
.col-m-12 {
width: 100%;
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
/* For desktop: */
.col-1 {
width: 8.33%;
}
.col-2 {
width: 16.66%;
}
.col-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-4 {
width: 33.33%;
}
.col-5 {
width: 41.66%;
}
.col-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-7 {
width: 58.33%;
}
.col-8 {
width: 66.66%;
}
.col-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-10 {
width: 83.33%;
}
.col-11 {
width: 91.66%;
}
.col-12 {
width: 100%;
}
}以上代码看起来很多余,但是他可以根据屏幕大小自动设置不同的样式,所以还是非常必要的。
针对桌面设备: 第一和第三部分跨越 3 列。中间部分跨域 6 列。 针对平板设备: 第一跨域 3 列,第二部分跨越 9 列,第三部分跨域 12 列:
<div class="row">
<div class="col-3 col-m-3">...</div>
<div class="col-6 col-m-9">...</div>
<div class="col-3 col-m-12">...</div >
</div>orientation:portrait | landscape@media only screen and (orientation: landscape) {
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
}`max-width` 属性
如果 `max-width` 属性设置为 100%, 图片永远不会大于其原始大小:
img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto; }大尺寸图片可以显示在大屏幕上,但在小屏幕上确不能很好显示。我们没有必要在小屏幕上去加载大图片,这样很影响加载速度。所以我们可以使用媒体查询,根据不同的设备显示不同的图
/* For width smaller than 400px: */
body {
background-image: url('img_smallflower.jpg');
}
/* For width 400px and larger: */
@media only screen and (min-width: 400px) {
body {
background-image: url('img_flowers.jpg'); } }可以使用媒体查询的 min-device-width 替代 min-width 属性,它将检测的是设备宽度而不是浏览器宽度。浏览器大小重置时,图片大小不会改变。
/* 设备小于 400px: */
body {
background-image: url('img_smallflower.jpg'); }
/* 设备大于 400px (也等于): */
@media only screen and (min-device-width: 400px) {
body {
background-image: url('img_flowers.jpg'); } }如果max-width 属性设置为 100%, 视频播放器会根据屏幕自动调整比例,但不会超过其原始大小:
video {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}div {
border: 2px solid;
border-radius: 25px;
}div {
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #888888;
}div {
border-image: url(border.png) 30 30 round;
-webkit-border-image: url(border.png) 30 30 round; /* Safari 5 and older */
-o-border-image: url(border.png) 30 30 round; /* Opera */
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>W3Cschool在线教程(w3cschool.cn)</title>
<style>
#rcorners1 {
border-radius: 25px;
background: #8ac007;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
}
#rcorners2 {
border-radius: 25px;
border: 2px solid #8ac007;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
}
#rcorners3 {
border-radius: 25px;
background: url(/statics/images/course/paper.gif);
background-position: left top;
background-repeat: repeat;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>border-radius 属性允许向元素添加圆角。</p>
<p>指定背景颜色元素的圆角:</p>
<p id="rcorners1">圆角</p>
<p>指定边框元素的圆角:</p>
<p id="rcorners2">圆角</p>
<p>指定背景图片元素的圆角:</p>
<p id="rcorners3">圆角</p>
</body>
</html>border-radius 所有四个边角 border---radius 属性的缩写
border-top-left-radius 定义了左上角的弧度
border-top-right-radius 定义了右上角的弧度
border-bottom-right-radius 定义了右下角的弧度
border-bottom-left-radius 定义了左下角的弧度
#example1 {
background-image: url(img_flwr.gif), url(paper.gif);
background-position: right bottom, left top;
background-repeat: no-repeat, repeat;
}#example1 {
background: url(img_flwr.gif) right bottom no-repeat, url(paper.gif) left
top repeat;
}div {
background: url(img_flwr.gif);
background-size: 80px 60px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}div {
background: url(img_flwr.gif);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: 100% 100%;
background-origin: content-box;
}#example1 {
border: 10px dotted black;
padding: 35px;
background: yellow;
background-clip: content-box;
}为了创建一个线性渐变,你必须至少定义两种颜色结点。颜色结点即你想要呈现平稳过渡的颜色。同时,你也可以设置一个起点和一个方向(或一个角度)

background: linear-gradient(direction, color-stop1, color-stop2, ...);线性渐变 - 从上到下(默认情况下) 下面的实例演示了从顶部开始的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到蓝色
#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(red, blue);
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(red, blue);
/* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-linear-gradient(red, blue);
/* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: linear-gradient(red, blue);
/* 标准的语法 */
}线性渐变 - 从左到右 下面的实例演示了从左边开始的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到蓝色
#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, red , blue);
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(right, red, blue);
/* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, red, blue); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: linear-gradient(to right, red , blue);
/* 标准的语法 */
}线性渐变 - 对角 你可以通过指定水平和垂直的起始位置来制作一个对角渐变。 下面的实例演示了从左上角开始(到右下角)的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到蓝色
#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left top, red , blue); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, blue); /* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, blue); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: linear-gradient(to bottom right, red , blue); /* 标准的语法 */
}如果你想要在渐变的方向上做更多的控制,你可以定义一个角度,而不用预定义方向(to bottom、to top、to right、to left、to bottom right,等等)
background: linear-gradient(angle, color-stop1, color-stop2);角度是指水平线和渐变线之间的角度,顺时针方向计算。换句话说,0deg 将创建一个从下到上的渐变,90deg 将创建一个从左到右的渐变。

但是,请注意很多浏览器(Chrome,Safari,fiefox 等)的使用了旧的标准,即 0deg 将创建一个从下到上的渐变,90deg 将创建一个从左到右的渐变。换算公式 90 - x = y 其中 x 为标准角度,y 为非标准角度。
#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(180deg, red, blue); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(180deg, red, blue); /* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-linear-gradient(180deg, red, blue); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: linear-gradient(180deg, red, blue); /* 标准的语法 */
}#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-linear-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: linear-gradient(red, green, blue); /* 标准的语法 */
}CSS3 渐变也支持透明度(transparency),可用于创建减弱变淡的效果。 为了添加透明度,我们使用 rgba() 函数来定义颜色结点。rgba() 函数中的最后一个参数可以是从 0 到 1 的值,它定义了颜色的透明度:0 表示完全透明,1 表示完全不透明。 下面的实例演示了从左边开始的线性渐变。起点是完全透明,慢慢过渡到完全不透明的红色
#grad {
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left,rgba(255,0,0,0),rgba(255,0,0,1)); /* Safari 5.1 - 6 */
background: -o-linear-gradient(right,rgba(255,0,0,0),rgba(255,0,0,1)); /* Opera 11.1 - 12*/
background: -moz-linear-gradient(right,rgba(255,0,0,0),rgba(255,0,0,1)); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15*/
background: linear-gradient(to right, rgba(255,0,0,0), rgba(255,0,0,1)); /* 标准的语法 */
}repeating-linear-gradient() 函数用于重复线性渐变
#grad {
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -webkit-repeating-linear-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 20%);
/* Opera 11.1 - 12.0 */
background: -o-repeating-linear-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 20%);
/* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: -moz-repeating-linear-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 20%);
/* 标准的语法 */
background: repeating-linear-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 20%);
}径向渐变由它的中心定义。
为了创建一个径向渐变,你也必须至少定义两种颜色结点。颜色结点即你想要呈现平稳过渡的颜色。同时,你也可以指定渐变的中心、形状(圆形或椭圆形)、大小。默认情况下,渐变的中心是 center(表示在中心点),渐变的形状是 ellipse(表示椭圆形),渐变的大小是 farthest-corner(表示到最远的角落)。
径向渐变的实例:

background: radial-gradient(center, shape size, start-color, …, last-color); 径向渐变 - 颜色结点均匀分布(默认情况下)
#grad {
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-radial-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-radial-gradient(red, green, blue); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: radial-gradient(red, green, blue); /* 标准的语法 */
}径向渐变 - 颜色结点不均匀分布
#grad {
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(red 5%, green 15%, blue 60%); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-radial-gradient(red 5%, green 15%, blue 60%); /* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-radial-gradient(red 5%, green 15%, blue 60%); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: radial-gradient(red 5%, green 15%, blue 60%); /* 标准的语法 */
}shape 参数定义了形状。它可以是值 circle 或 ellipse。其中,circle 表示圆形,ellipse 表示椭圆形。默认值是 ellipse
#grad {
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green); /* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -o-radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green); /* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -moz-radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green); /* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green); /* 标准的语法 */
}size 参数定义了渐变的大小。它可以是以下四个值:
#grad1 {
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(60% 55%, closest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -o-radial-gradient(60% 55%, closest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: -moz-radial-gradient(60% 55%, closest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* 标准的语法 */
background: radial-gradient(60% 55%, closest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
}
#grad2 {
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(60% 55%, farthest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -o-radial-gradient(60% 55%, farthest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: -moz-radial-gradient(60% 55%, farthest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
/* 标准的语法 */
background: radial-gradient(60% 55%, farthest-side,blue,green,yellow,black);
}repeating-radial-gradient() 函数用于重复径向渐变
#grad {
/* Safari 5.1 - 6.0 */
background: -webkit-repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
/* Opera 11.6 - 12.0 */
background: -o-repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
/* Firefox 3.6 - 15 */
background: -moz-repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
/* 标准的语法 */
background: repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
}h1
{
text-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #FF0000;
}div { box-shadow: 10px 10px;}
div { box-shadow: 10px 10px grey;}
div { box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px grey ;} <* 添加模糊效果 *>阴影的一个使用特例是卡片效果
div.card {
width: 250px;
box-shadow:
0 4px 8px 0
rgba(0 ,0, 0, 0.2),
0 6px 20px 0
rgba (0, 0, 0, 0.19) ;
text-align: center;
}p.test1 {
white-space: nowrap;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: clip;
}
p.test2 {
white-space: nowrap;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}p {
word-wrap: break-word;
}p.test1 {
word-break: keep-all;
}
p.test2 {
word-break: break-all;
}在新的 @font-face 规则中,您必须首先定义字体的名称(比如 myFirstFont),然后指向该字体文件。
> **提示:URL 请使用小写字母的字体,大写字母在 IE 中会产生意外的结果
如果需要为 HTML 元素使用字体,请通过 font-family 属性来引用字体的名称 (myFirstFont),通过下面的实例您可以尝试操作一下
<style>
@font-face
{
font-family: myFirstFont;
src: url(sansation_light.woff);
}
div
{
font-family:myFirstFont;
}
</style>@font-face
{
font-family: myFirstFont;
src: url(sansation_bold.woff);
font-weight:bold;
}下表列出了所有的字体描述和里面的 @font-face 规则定义:
| 描述符 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| font-family | name | 必需。规定字体的名称。 |
| src | URL | 必需。定义字体文件的 URL。 |
| font-stretch |
| 可选。定义如何拉伸字体。默认是 "normal"。 |
| font-style |
| 可选。定义字体的样式。默认是 "normal"。 |
| font-weight |
| 可选。定义字体的粗细。默认是 "normal"。 |
| unicode-range | unicode-range | 可选。定义字体支持的 UNICODE 字符范围。默认是 "U+0-10FFFF"。 |
CSS3 过渡是元素从一种样式逐渐改变为另一种的效果 必须规定两项内容:
应用于宽度属性的过渡效果,时长为 2 秒:
div {
transition: width 2s;
-webkit-transition: width 2s; /* Safari */
}当鼠标指针悬浮(:hover)于 <div>元素上时
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
transition: width 2s;
-webkit-transition: width 2s; /* Safari */
}
div:hover {
width: 300px;
}要添加多个样式的变换效果,添加的属性由逗号分隔 添加了宽度,高度和转换效果
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
-webkit-transition: width 2s, height 2s, -webkit-transform 2s; /* For Safari 3.1 to 6.0 */
transition: width 2s, height 2s, transform 2s;
}
div:hover {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
-webkit-transform: rotate(180deg); /* Chrome, Safari, Opera */
transform: rotate(180deg);
}div {
transition-property: width;
transition-duration: 1s;
transition-timing-function: linear;
transition-delay: 2s;
/* Safari */
-webkit-transition-property: width;
-webkit-transition-duration: 1s;
-webkit-transition-timing-function: linear;
-webkit-transition-delay: 2s;
}@keyframes 规则是创建动画。 @keyframes 规则内指定一个 CSS 样式和动画将逐步从目前的样式更改为新的样式
@keyframes myfirst {
from {
background: red;
}
to {
background: yellow;
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */ {
from {
background: red;
}
to {
background: yellow;
}
}当在@keyframe 创建动画,把它绑定到一个选择器,否则动画不会有任何效果。 指定至少这两个 CSS3 的动画属性绑定向一个选择器:
myfirst” 动画捆绑到 div 元素,时长:5 秒:div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
animation: myfirst 5s;
-webkit-animation: myfirst 5s; /* Safari and Chrome */
}
@keyframes myfirst {
from {
background: red;
}
to {
background: yellow;
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */ {
from {
background: red;
}
to {
background: yellow;
}
}动画是使元素从一种样式逐渐变化为另一种样式的效果。 您可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数。
请用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用关键词 “from” 和 “to”,等同于 0% 和 100%。
0% 是动画的开始,100% 是动画的完成。
为了得到最佳的浏览器支持,您应该始终定义 0% 和 100% 选择器
当动画为 25% 及 50% 时改变背景色,然后当动画 100% 完成时再次改变
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
animation: myfirst 5s;
-moz-animation: myfirst 5s; /* Firefox */
-webkit-animation: myfirst 5s; /* Safari and Chrome */
-o-animation: myfirst 5s; /* Opera */
}
@keyframes myfirst {
0% {
background: red;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
}
50% {
background: blue;
}
100% {
background: green;
}
}
@-moz-keyframes myfirst /* Firefox */ {
0% {
background: red;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
}
50% {
background: blue;
}
100% {
background: green;
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */ {
0% {
background: red;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
}
50% {
background: blue;
}
100% {
background: green;
}
}
@-o-keyframes myfirst /* Opera */ {
0% {
background: red;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
}
50% {
background: blue;
}
100% {
background: green;
}
}改变背景色和位置
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position: relative;
animation: myfirst 5s;
-webkit-animation: myfirst 5s; /* Safari and Chrome */
}
@keyframes myfirst {
0% {
background: red;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
left: 200px;
top: 0px;
}
50% {
background: blue;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}
75% {
background: green;
left: 0px;
top: 200px;
}
100% {
background: red;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */ {
0% {
background: red;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
25% {
background: yellow;
left: 200px;
top: 0px;
}
50% {
background: blue;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}
75% {
background: green;
left: 0px;
top: 200px;
}
100% {
background: red;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
}所有属性
div {
animation-name: myfirst;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-timing-function: linear;
animation-delay: 2s;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
animation-direction: alternate;
animation-play-state: running;
/* Safari and Chrome: */
-webkit-animation-name: myfirst;
-webkit-animation-duration: 5s;
-webkit-animation-timing-function: linear;
-webkit-animation-delay: 2s;
-webkit-animation-iteration-count: infinite;
-webkit-animation-direction: alternate;
-webkit-animation-play-state: running;
}div
{
resize:both;
overflow:auto;
}div
{
box-sizing:border-box;
-moz-box-sizing:border-box; /* Firefox */
width:50%;
float:left;
}div
{
border:2px solid black;
outline:2px solid red;
outline-offset:15px;
}img {
border-radius: 8px;
}
img {
border-radius: 50%;
}
img {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 5px;
}
<img src="paris.jpg" alt="Paris">
body {
margin: 25px;
}
div.polaroid {
width: 80%;
background-color: white;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 6px 20px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.19);
margin-bottom: 25px;
}
div.container {
text-align: center;
padding: 10px 20px;
}img {
-webkit-filter: grayscale(100%); /* Chrome, Safari, Opera */
filter: grayscale(100%);
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>W3Cschool教程(w3cschool.cn)</title>
<style>
div.img {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
div.img:hover {
border: 1px solid #777;
}
div.img img {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
div.desc {
padding: 15px;
text-align: center;
}
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.responsive {
padding: 0 6px;
float: left;
width: 24.99999%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 700px) {
.responsive {
width: 49.99999%;
margin: 6px 0;
}
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 500px) {
.responsive {
width: 100%;
}
}
.clearfix:after {
content: "";
display: table;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 style="text-align:center">响应式图片相册</h2>
<div class="responsive">
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="img_fjords.jpg"
>
<img
src="/statics/images/course/img_fjords.jpg"
alt="Trolltunga Norway"
width="300"
height="200"
/>
</a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="responsive">
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="img_forest.jpg"
>
<img
src="/statics/images/course/img_forest.jpg"
alt="Forest"
width="600"
height="400"
/>
</a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="responsive">
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="img_lights.jpg"
>
<img
src="/statics/images/course/img_lights.jpg"
alt="Northern Lights"
width="600"
height="400"
/>
</a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="responsive">
<div class="img">
<a
target="_blank"
href="img_mountains.jpg"
>
<img
src="/statics/images/course/img_mountains.jpg"
alt="Mountains"
width="600"
height="400"
/>
</a>
<div class="desc">Add a description of the image here</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="clearfix"></div>
<div style="padding:6px;">
<h4>重置浏览器大小查看效果</h4>
</div>
</body>
</html>.button {
background-color: #4CAF50; /* Green */
color: white;
padding: 15px 32px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 2px solid #4CAF50; /* Green */
}.button {
-webkit-transition-duration: 0.4s; /* Safari */
transition-duration: 0.4s;
}
.button:hover {
background-color: #4CAF50; /* Green */
color: white;
}.button1 {
box-shadow: 0 8px 16px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.2), 0 6px 20px 0rgba(0,0,0,0.19);
}
.button2:hover {
box-shadow: 0 12px16px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.24), 0 17px 50px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.19);
}<style>
.button {
display: inline-block;
border-radius: 4px;
background-color: #f4511e;
border: none;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
transition: all 0.5s;
cursor: pointer;
margin: 5px;
}
.button span {
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
transition: 0.5s;
}
.button span:after {
content: "»";
position: absolute;
opacity: 0;
top: 0;
right: -20px;
transition: 0.5s;
}
.button:hover span {
padding-right: 25px;
}
.button:hover span:after {
opacity: 1;
right: 0;
}
</style><style>
.button {
position: relative;
background-color: #4CAF50;
border: none;
font-size: 28px;
color: #FFFFFF;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
-webkit-transition-duration: 0.4s; /* Safari */
transition-duration: 0.4s;
text-decoration: none;
overflow: hidden;
cursor: pointer;
}
.button:after {
content: "";
background: #90EE90;
display: block;
position: absolute;
padding-top: 300%;
padding-left: 350%;
margin-left: -20px!important;
margin-top: -120%;
opacity: 0;
transition: all 0.8s
}
.button:active:after {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
opacity: 1;
transition: 0s
}
</style><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>W3Cschool教程(w3cschool.cn)</title>
<style>
ul.pagination {
display: inline-block;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
ul.pagination li {display: inline;}
ul.pagination li a {
color: black;
float: left;
padding: 8px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>简单的分页</h2>
<ul class="pagination">
<li><a href="#">«</a></li>
<li><a href="#">1</a></li>
<li><a class="active" href="#">2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">3</a></li>
<li><a href="#">4</a></li>
<li><a href="#">5</a></li>
<li><a href="#">6</a></li>
<li><a href="#">7</a></li>
<li><a href="#">»</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>弹性盒子由弹性容器(Flex container)和弹性子元素(Flex item)组成。 弹性容器通过设置 display 属性的值为 flex 或 inline-flex 将其定义为弹性容器。 弹性容器内包含了一个或多个弹性子元素。 注意:弹性容器外及弹性子元素内是正常渲染的。弹性盒子只定义了弹性子元素如何在弹性容器内布局。 弹性子元素通常在弹性盒子内一行显示。默认情况每个容器只有一行。 以下元素展示了弹性子元素在一行内显示,从左到右
<div
class="flex-container"
> <div
class="flex-item"
> flex
item
1</div
> <div
class="flex-item"
> flex
item
2</div
> <div
class="flex-item"
> flex
item
3</div
> </div
> .flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
}flex-direction 顺序指定了弹性子元素在父容器中的位置。
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;flex-direction的值有:
.flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
-webkit-flex-direction: row-reverse;
flex-direction: row-reverse | row | column | column-reverse;
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
}内容对齐(justify-content)属性应用在弹性容器上,把弹性项沿着弹性容器的主轴线(main axis,也可理解为横轴)对齐。
内容对齐可以理解为弹性盒子的Y 轴坐标不变,盒子只会有 X 轴的变化,所以实际上内容对齐用于设置列对齐。像 flex-start 效果就有点像左对齐。 justify-content 语法如下:
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around;各个值解析:
.flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
-webkit-justify-content: center;
justify-content: center;
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}align-items (项目对齐)设置或检索弹性盒子元素在侧轴(纵轴)方向上的对齐方式。
项目对齐可以理解为弹性盒子的 X 轴坐标不变,盒子只会有 Y 轴的变化,所以实际上内容对齐用于设置行对齐。
align-items 属性可以理解为纵向的 justify-content
像center 效果就是垂直方向的居中。
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;各个值解析:
.flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
-webkit-align-items: stretch;
align-items: stretch;
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}flex-wrap 属性用于指定弹性盒子的子元素换行方式。
flex-wrap: nowrap|wrap|wrap-reverse|initial|inherit;各个值解析:
.flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
-webkit-flex-wrap: nowrap;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}align-content 属性用于修改 flex-wrap 属性的行为。类似于 align-items, 但它不是设置弹性子元素的对齐,而是设置各个行的对齐。
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around |
stretch;各个值解析:
stretch - 默认。各行将会伸展以占用剩余的空间。flex-start - 各行向弹性盒容器的起始位置堆叠。flex-end - 各行向弹性盒容器的结束位置堆叠。center -各行向弹性盒容器的中间位置堆叠。space-between -各行在弹性盒容器中平均分布。space-around - 各行在弹性盒容器中平均分布,两端保留子元素与子元素之间间距大小的一半。.flex-container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
-webkit-flex-wrap: wrap;
flex-wrap: wrap;
-webkit-align-content: center;
align-content: center;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightgrey;
}<integer>:没有设置 order 属性的顺序值默认为 0.
负值在前,然后默认为 0,正值最后,顺序值越小越在前面
order 属性设置弹性容器内弹性子元素的属性.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
}
.first {
-webkit-order: -1;
order: -1;
}设置”margin”值为”auto”值,自动获取弹性容器中剩余的空间。所以设置垂直方向 margin 值为”auto”,可以使弹性子元素在弹性容器的两上轴方向都完全集中。
以下实例在第一个弹性子元素上设置了 margin-right: auto; 。 它将剩余的空间放置在元素的右侧
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 75px;
height: 75px;
margin: 10px;
}
.flex-item:first-child {
margin-right: auto;
}以下实例将完美解决我们平时碰到的居中问题。
使用弹性盒子,居中变的很简单,只想要设置 margin: auto; 可以使得弹性子元素在两上轴方向上完全居中
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 75px;
height: 75px;
margin: auto;
}align-self 属性用于设置弹性元素自身在侧轴(纵轴)方向上的对齐方式。
align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;各个值解析:
以下实例演示了弹性子元素上 align-self 不同值的应用效果 ![[微信截图_20230324232208.png]]
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
width: 60px;
min-height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
}
.item1 {
-webkit-align-self: flex-start;
align-self: flex-start;
}
.item2 {
-webkit-align-self: flex-end;
align-self: flex-end;
}
.item3 {
-webkit-align-self: center;
align-self: center;
}
.item4 {
-webkit-align-self: baseline;
align-self: baseline;
}
.item5 {
-webkit-align-self: stretch;
align-self: stretch;
}flex 属用于指定弹性子元素如何分配空间。
flex:none | [ flex-grow ] || [ flex-shrink ] || [ flex-basis ]各个值解析:
.flex-item {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
margin: 10px;
}
.item1 {
-webkit-flex: 2;
flex: 2;
}
.item2 {
-webkit-flex: 1;
flex: 1;
}
.item3 {
-webkit-flex: 1;
flex: 1;
}